Customize file import rules
In Matecat, you can control how files are processed before translation. To access these options, open the Settings panel and go to the File Import tab.
Segmentation rules
You can choose among three segmentation rules, depending on how you want Matecat to split the text into segments. Select the desired option from the drop-down menu:

- General: Generates a new segment at the end of each layout element (e.g. a paragraph, a table cell etc.) and every time a strong punctuation mark is detected (e.g. full stop, exclamation mark).
- Patent: Works like the general rule but includes exceptions for abbreviations commonly used in patents.
- Paragraph: Generates a new segment only at the end of layout elements such as paragraphs, table cells, and bullet points.
Extraction parameters
From the Extraction parameters section, you can customize how Matecat processes specific file formats during import.

When you modify the default extraction parameters, Matecat prompts you to save the changes, either as a new configuration, or, if you are editing an existing configuration, as a new version of it.
Even if you don’t save the configuration, the new settings are still applied to the project you are currently creating.
To use custom extraction parameters in a project template, first save the settings in a configuration (either new or existing).
If you create a new configuration or edit an existing one that is not yet linked to the current project template, link the configuration to the template and save the template.
If you edit a configuration that is already linked to the current project template, you don’t need to save the template again, as the changes take effect automatically.
Depending on the file format, different extraction options are available. Use them to customize how Matecat handles the content during import.
JSON
- Translate arrays: When active, text values in arrays are extracted for translation. Can be used in combination with the “Translatable keys” parameter.
- Escape forward slashes: When active, forward slashes in the target file are escaped with one backslash; thus, "\" in Matecat's editor becomes "\/" in the target file.
- Translatable keys: When set to 'Translatable,' Matecat extracts only the keys entered in the text box. When set to 'Non-translatable,' it extracts all keys except those specified. If the text box is empty, all keys are extracted. Key names are case-sensitive. The text box supports key names and full or partial paths (for more details, refer to the 'How to extract the right content' section below).
- Context keys: Matecat extracts the keys entered in the text box as context for translatable keys in the same object scope. Key names are case-sensitive. The text box supports key names and full or partial paths (for more details, refer to the 'How to extract the right content' section below).
- Character limit keys: Matecat extracts the keys entered in the text box as the character limit for translatable keys in the same object scope. Key names are case-sensitive. The text box supports key names and full or partial paths. For more details, refer to the 'How to extract the right content' section below.
XML
- Preserve whitespaces: When active, whitespaces in translatable elements are preserved; equivalent to globally applying the local xml:space attribute.
- Translatable elements: When set to 'Translatable,' Matecat extracts only the elements entered in the text box. When set to 'Non-translatable,' it extracts all elements except those specified. If the text box is empty, all elements are extracted. Element names are case-sensitive. The text box supports element names and full or partial paths (for more details, refer to the 'How to extract the right content' section below).
- Translatable attributes: Matecat extracts for translation the names of attributes entered in the text box. The format for each element should be: elementname@attributename.
YAML
- Translatable keys: When set to 'Translatable,' Matecat extracts only the keys entered in the text box. When set to 'Non-translatable,' it extracts all keys except those specified. If the text box is empty, all keys are extracted. Key names are case-sensitive. The text box supports key names and full or partial paths (for more details, refer to the 'How to extract the right content' section below).
- Context keys: Choose which keys should be extracted as context for translatable keys. Key names are case-sensitive. The extracted notes will be applied to translatable keys that are siblings within the same mapping (that is, keys indented to the same level under the same parent key).
- Character limit keys: Choose which keys should be extracted as character limits for translatable keys. Key names are case-sensitive. Character limits will be applied to translatable keys that are siblings within the same mapping (that is, keys indented to the same level under the same parent key).
- Translatable text content type: Select the content type of the translatable text to optimize segmentation and tag handling.
MS Word
- Translate headers and footers: When active, text in headers and footers is extracted for translation.
- Translate hidden text: When active, any hidden text in the file is extracted for translation.
- Translate comments: When active, any comments in the file are extracted for translation.
- Translate document properties: When active, the file’s properties (e.g. the author’s name) are extracted for translation.
- Automatically accept revisions: When active, all revisions in the file are accepted before project creation. If inactive, an error appears when the file is uploaded, prompting you to review the revisions and accept or reject them.
- Exclude styles: Matecat excludes from translation any text with the styles specified in the text box. Style names are case-sensitive. For styles with names consisting of multiple words, remove the whitespaces; for example, if a style's name is 'test Style,' enter it in the text box as 'testStyle'.
- Exclude highlight colors: Matecat excludes from translation any text highlighted with the colors specified in the text box. Key names are case-sensitive. A list of default highlight color names is available below.
|
MS Word 2007-365 (DOCX) |
MS Word 97-2003 (DOC) |
|
yellow |
yellow |
|
green |
green |
|
cyan |
cyan |
|
magenta |
magenta |
|
red |
red |
|
darkBlue |
darkBlue |
|
darkGreen |
darkGreen |
|
darkYellow |
darkYellow |
|
black |
black |
|
blue |
N.A. |
|
darkCyan |
N.A. |
|
darkMagenta |
N.A. |
|
darkGrey |
N.A. |
|
lightGrey |
N.A. |
MS Excel
- Translate hidden cells: when active, any hidden cells in the file are extracted for translation.
- Translate chart texts: When active, any chart texts in the file are extracted for translation.
- Translate text boxes: When active, any text boxes in the file are extracted for translation.
- Translate document properties: When active, the file's properties (e.g., the author's name) are extracted for translation.
- Exclude columns: Matecat excludes from translation any column specified in the text box. Format the entered items as sheet number + column letter; for example, enter 1C to exclude column C of the first sheet from the translation.
MS PowerPoint
- Translate hidden slides: When active, any hidden slides in the file are extracted for translation. This option is mutually exclusive with the 'Translatable slides' option.
- Translate speaker notes: When active, all speaker notes are extracted for translation, including notes for hidden slides not being extracted. However, if activated in combination with the 'Translatable slides' option, only the notes for the listed slides are extracted.
- Translate document properties: When active, the file's properties (e.g., the author's name) are extracted for translation.
- Translatable slides: Matecat extracts for translation only the slides specified in the text box. If the text box is empty, all slides in the file are extracted for translation. The text box also accepts slide ranges expressed as numbers separated by hyphens (e.g., 2–4, 6, 8–10).
DITA/DITAMAP
- Non-translatable elements: When importing DITA or DITAMAP files, you can specify which elements should not be translated.If the field is left empty, only elements marked as translatable according to the DITA specification will be extracted. Element names are case-sensitive.
Xliff import settings
For source files in XLIFF format, you can customize how Matecat handles segments based on their state or state-qualifier.
For XLIFF 1.2 files, you can define behavior according to the state and state-qualifier values specified in the standard. State-qualifiers take precedence over states. Therefore, if you have set a specific behavior for segments with the ‘translated’ state and a different behavior for those with the ‘exact-match’ state-qualifier, a segment marked with both will be processed according to the ‘exact-match’ state-qualifier.
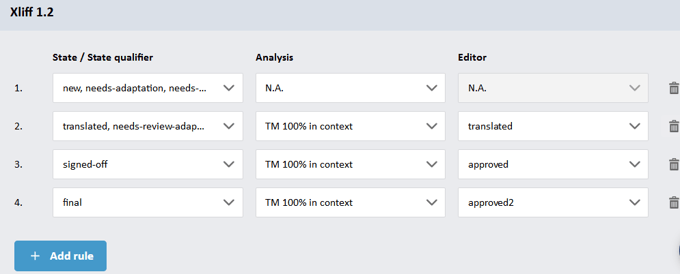
For XLIFF 2.0 files, behavior selection is limited to the state values listed in the standard.
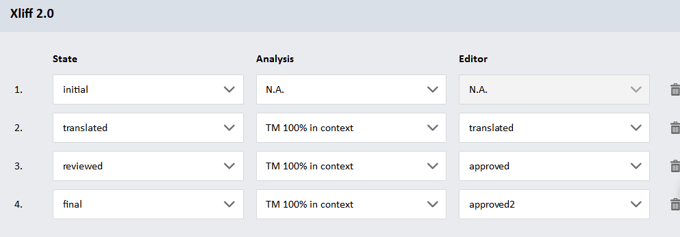
Custom state and state-qualifier values are not supported and will be ignored.
For each state/state-qualifier value, you can decide whether a segment’s target content should be ignored or not:
- If you choose to ignore the target content, the segment will undergo the regular Translation Memory (TM) analysis process. Its analysis bucket and state in Matecat’s editor will be determined by matches found in the translation memories linked to the job.
- If you choose to consider the target content, you can select the analysis bucket for the segment and define the state it should have within Matecat’s editor.
The rules in the default settings configuration represent Matecat’s default handling of segments in XLIFF files.
You can modify, remove or create new rules to tailor Matecat’s behavior to your needs.
When you modify the default import settings, Matecat prompts you to save the changes, either as a new configuration, or, if you are editing an existing configuration, as a new version of it.
Even if you don’t save the configuration, the new settings are still applied to the project you are currently creating.
To use custom import settings in a project template, first save the settings in a configuration (either new or existing).
If you create a new configuration or edit an existing one that is not yet linked to the current project template, link the configuration to the template and save the template.
If you edit a configuration that is already linked to the current project template, you don’t need to save the template again, as the changes take effect automatically.
How to extract the right content
This paragraph includes instructions for the following extraction parameters:
- JSON: Translatable keys, Context keys, Character limit keys
- XML: Translatable elements
- YAML: Translatable keys, Context keys, Character limit keys
- DITA / DITAMAP: Non-translatable elements
These extraction parameters support specific key or element names and paths as values in the text box.
For JSON files, only key names must be entered, without quotation marks around it.
Example
If you want keys called ‘text’ to be extracted as translatable, you should only enter text in the relevant field, not “text”.
For XML and DITA/DITAMAP files, only element names must be entered, without quotation marks around it, and attributes must be ignored.
Example
If you want elements called ‘text’ to be extracted as translatable, you should only enter text in the relevant field, not <text>, and avoid adding any attributes.
When a key/element name is entered in the text box, Matecat extracts all keys/elements with that name.
Example
For JSON files, if 'text' is used as the value for 'Translatable keys', all keys named 'text' in the file will be extracted for translation.
When a path is entered, Matecat extracts all keys or elements that match that path. Paths should use a forward slash to divide hierarchical elements (e.g., level1/level2).
Example
For JSON files, if 'body/text' is used for 'Translatable keys', only keys named 'text' within a 'body' object will be extracted. A 'text' key under a 'heading' object will not be extracted.